Glucocorticoid
receptor
activation
and
chemotherapy
resistance




Chapters
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation and Chemotherapy Resistance
Leading oncologists like Robert L Coleman, MD, FACOG, FACS, discuss resistance in ovarian cancer.
- How does glucocorticoid receptor (GR) activation lead to chemotherapy resistance?1
- What role does the GR play in apoptosis?1

How cancer can evade apoptosis
Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling is a newly identified
resistance mechanism in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer2
Recurrent malignancies like platinum-resistant ovarian cancer use cellular-
signaling pathways to evade chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Glucocorticoid
receptor activation is a pathway that can reframe our understanding of ovarian
cancer chemotherapy resistance.2

GR activation starts
with cortisol
The stress hormone
Cortisol, commonly known as the stress
hormone, is an endogenous glucocorticoid
that plays an important role in a range of
cellular and physiological functions.3
GR activation in cancer
By activating the glucocorticoid receptor, cortisol
can promote tumor progression by suppressing
pro-apoptotic pathways used by cytotoxic agents.1
High glucocorticoid receptor expression in ovarian
cancer correlates with shorter progression-free
survival, and preclinical studies have shown the impact that physiological cortisol levels can have on chemotherapy-mediated cell death.1,4-6
Select publication

Melhem A, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2009.
Administration of glucocorticoids to ovarian cancer patients is associated with
expression of the anti-apoptotic genes SGK1 and MKP1/DUSP1 in ovarian tissues.
How GR activation can suppress apoptosis
Competing signals impact chemotherapy resistance
Research indicates that glucocorticoid receptor (GR) activation may reduce the activity of
chemotherapy in ovarian cancer cells. When activated, the GR promotes the expression of anti-
apoptotic genes which suppress the signaling pathways that taxanes utilize to induce microtubule
stabilization, mitotic arrest, and, ultimately, apoptosis.1,7
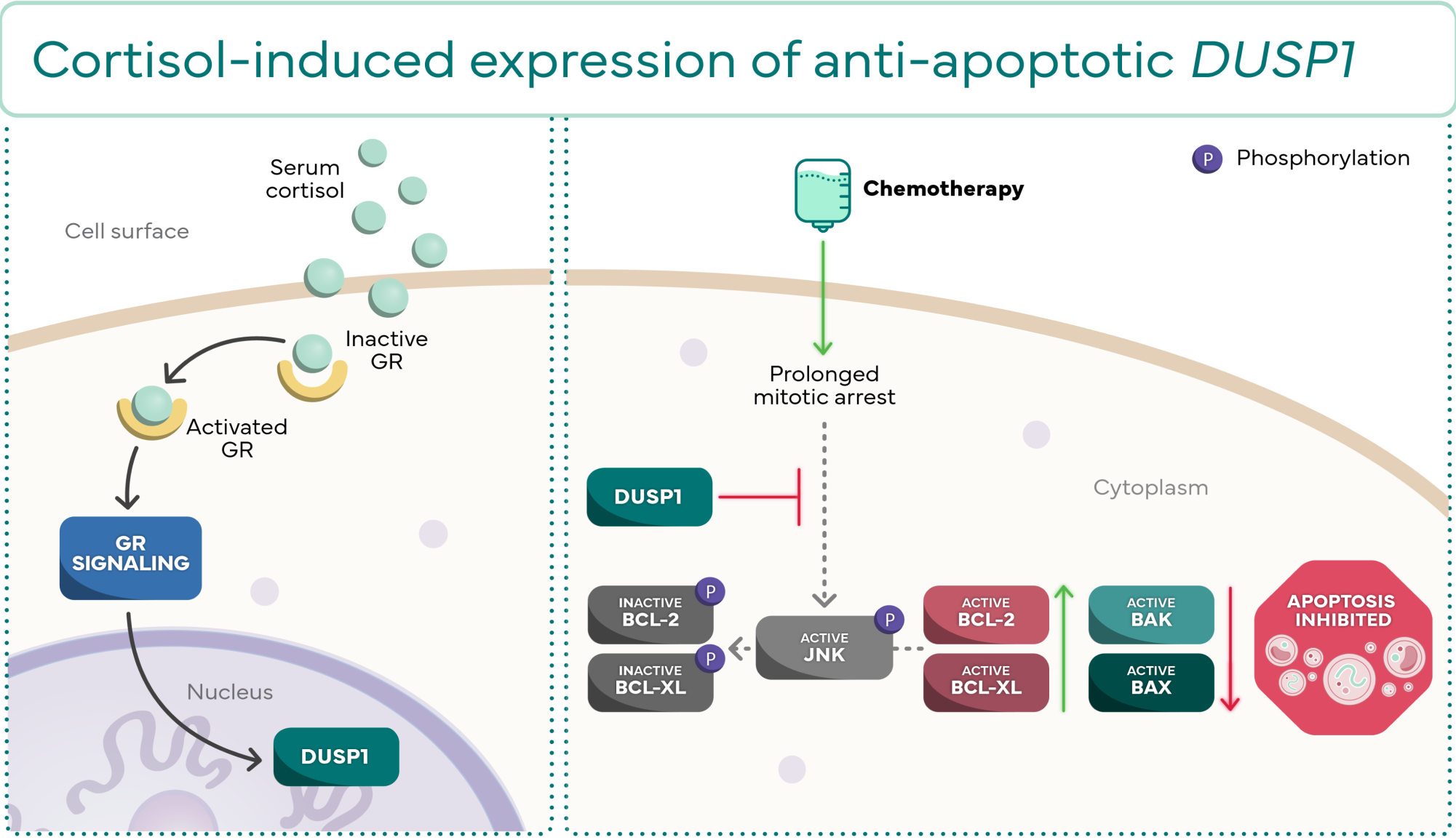
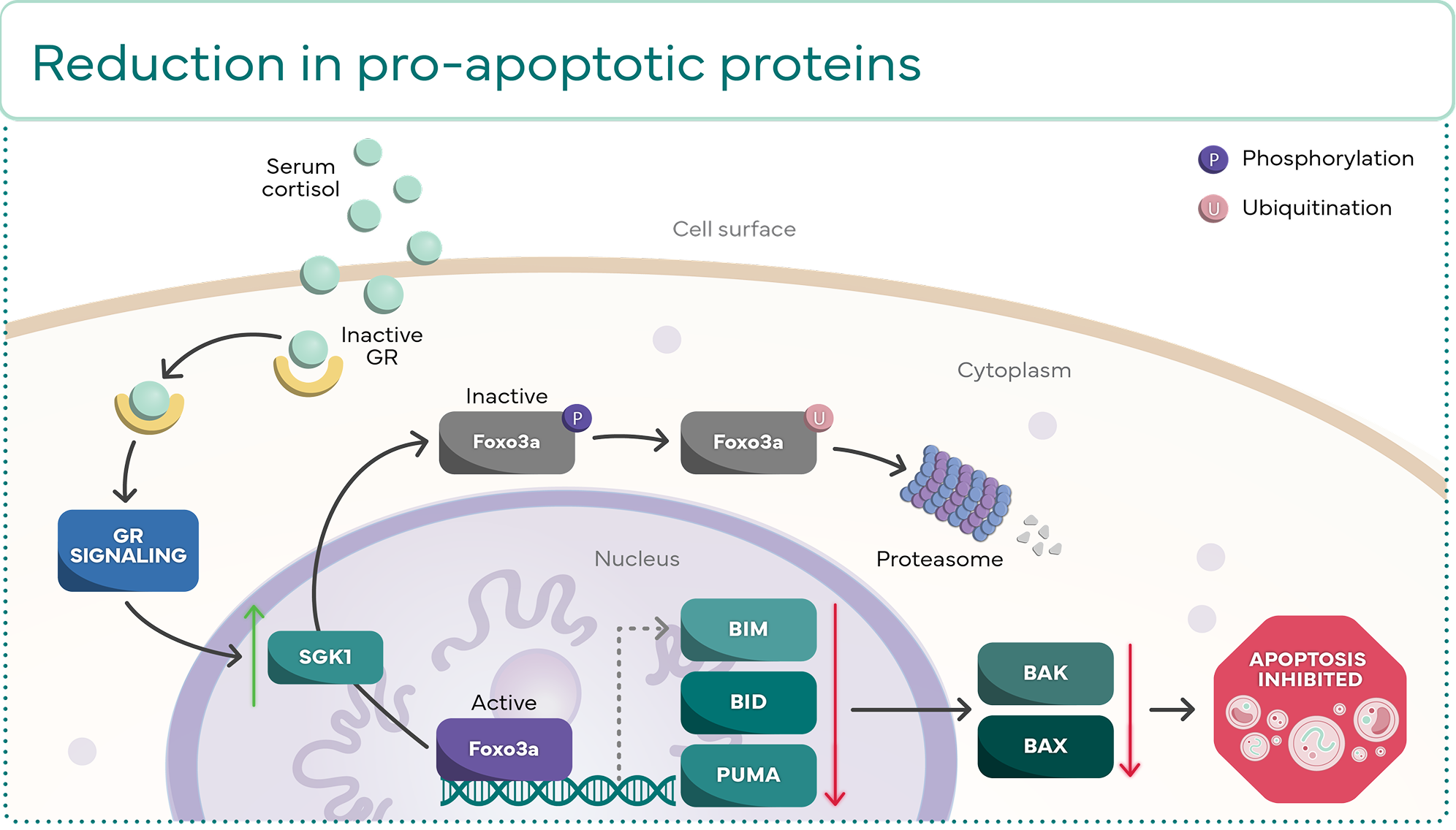
Molecular effects of DUSP1 and SGK1 expression
DUSP1 and SGK1 are 2 of the anti-apoptotic genes that can be expressed through GR
activation. They both act to prevent apoptosis through their own distinct molecular cascades.2

DUSP1
Increase in active anti-apoptotic proteins2,9-12


SGK1
Reduction in pro-apoptotic
proteins2,4,8,9,12-14
Evidence suggests GR activation has a key
role in treatment resistance4
Research is ongoing to further understand this key pathway, which is integral to the chemotherapy
resistance seen in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer and other solid tumors.2
References:
1. Greenstein AE, Hunt HJ. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism promotes apoptosis in solid tumor cells. Oncotarget. 2021;12(13):1243-1255. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.27989 2. Buonaiuto R, Neola G, Cecere SC, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor and ovarian cancer: from biology to therapeutic intervention. Biomolecules. 2023;13(4):653. doi:10.3390/biom13040653 3. Thau L, Gandhi J, Sharma S. Physiology, Cortisol. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; August 28, 2023. 4. Colombo N, Van Gorp T, Matulonis UA, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(30):4779-4789. 5. Veneris JT, Darcy KM, Mhawech-Fauceglia P, et al. High glucocorticoid receptor expression predicts short progression-free survival in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;146(1):153-160. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.04.012 6. Greenstein AE, Hunt HJ. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;120:110312. 7. Munster PN, Greenstein AE, Fleming GF, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(15):3214-3224. 8. Sang Y, Kong P, Zhang S, et al. SGK1 in human cancer: emerging roles and mechanisms. Front Oncol. 2021;10:608722. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.608722 9. Whitaker RH, Placzek WJ. Regulating the BCL2 family to improve sensitivity to microtubule targeting agents. Cells. 2019;8(4):346. doi:10.3390/cells8040346 10. Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 2008;27(48):6245-6251. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.301 11. Chen Y, Li N, Yang J, et al. PUMA overexpression dissociates thioredoxin from ASK1 to activate the JNK/BCL-2/BCL-XL pathway augmenting apoptosis in ovarian cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022;1868(12):166553. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166553 12. Pedley R, Gilmore AP. Mitosis and mitochondrial priming for apoptosis. Biol Chem. 2016;397(7):595-605. doi:10.1515/hsz-2016-0134 13. Liu Y, Ao X, Ding W, et al. Critical role of FOXO3a in carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):104. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0856-3 14. Mei W, Mei B, Chang J, et al. Role and regulation of FOXO3a: new insights into breast cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1346745. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1346745







